Curcumin nutritional supplements are among the top-selling supplements on the market and are widely popular because of curcumin’s numerous health-promoting benefits. Curcumin, the yellow pigment in turmeric, is an antioxidant that promotes the health of the heart, bones, muscles, liver, immune system, and gut.*
Several curcumin supplement formulations are available commercially, which can make selecting a high-quality supplement challenging. So what should you consider when searching for the best curcumin supplement? What are the features of an advanced curcumin formulation that can support your health and help meet your wellness goals?
In this guide, we’ll explore curcumin’s absorption challenges, features that make a formulation high-quality for achieving optimal benefits of curcumin supplements, and why including an advanced curcumin supplement in your regimen can support your health goals. Use the links below to jump ahead to different topics on the page.

Turmeric has been used for centuries across different cultures because of the health-promoting benefits of its main component, curcumin. Let’s understand how curcumin supplementation supports different health functions.
| The Health Benefits of Curcumin Supplementation | |
|---|---|
| Cardiovascular health | The cardioprotective benefits of curcumin are closely associated with its role in the signaling pathways involved in cellular proliferation, cell death, and the body’s inflammatory response.* Multiple systematic reviews1 indicate the ability of curcumin to help improve lipid profiles and maintain a normal cholesterol level.* |
| Musculoskeletal health | Curcumin promotes a healthy inflammatory response to non-chronic musculoskeletal and joint discomfort2. Several clinical trials indicate the role of curcumin in supporting joint health3. |
| Gastrointestinal health | Curcumin and its metabolites positively influence the gut microbiota by supporting the growth of beneficial bacteria strains, such as butyrate-producing bacteria.4 |
| Immune health | Curcumin is a potent immuno-supportive agent that up-regulates the activation of beneficial immune cells5. Curcumin down-regulates the expression of proinflammatory cytokines, the signaling molecules that can cause an imbalanced inflammatory response6.* |
| Hepatic health* | Studies indicate that curcumin helps lower lipid levels in the blood, which further limits the concentration of lipids and fatty acids in liver cells.7 The antioxidant properties of curcumin positively influence various cell signaling pathways, including the NF-κβ signaling pathway, that promote liver health8. |
The health-promoting effects of curcumin are attributed to its:
You might be using products that contain curcumin as a flavoring agent or as a coloring agent in teas, energy drinks, soaps, and cosmetics. Commercially available curcumin nutritional supplements are available in different forms for oral intake, as well as in topical applications.
| Types of Curcumin Products | ||
|---|---|---|
| Powders | Tablets | |
| Capsules | Liquid turmeric | |
| Sprays | Ointments | |
When you are looking for a high quality oral curcumin supplement, you should be aware of the common challenges with most formulations.
These factors contribute to the minimal absorption of curcumin and its rapid elimination from the body.
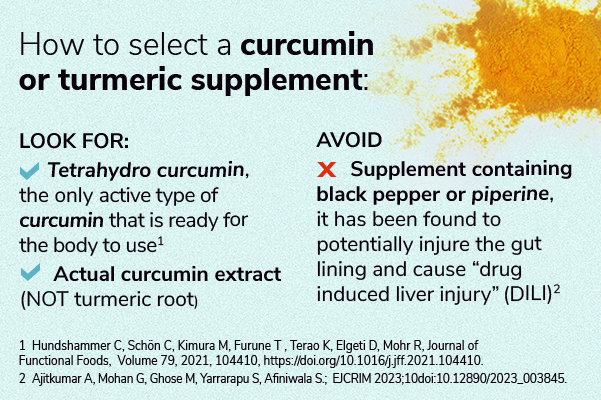
When considering a curcumin supplement, determine whether the formulation contains actual curcumin extract instead of whole turmeric root. Although turmeric root in a supplement formulation might seem all-natural, it would not achieve the desired benefit for the following reasons.
The following table highlights several key features of a high quality oral curcumin supplement:
| Key Features of A High Quality Oral Curcumin Supplement | ||
|---|---|---|
| Palatability: The formulation should be palatable to help achieve user compliance. | ||
| Absorption: The formulation should utilize a nutrient delivery system that optimizes the absorption of curcumin. | ||
| Bioavailability: The formulation should contain the most bioavailable form of curcumin for optimal solubility. |
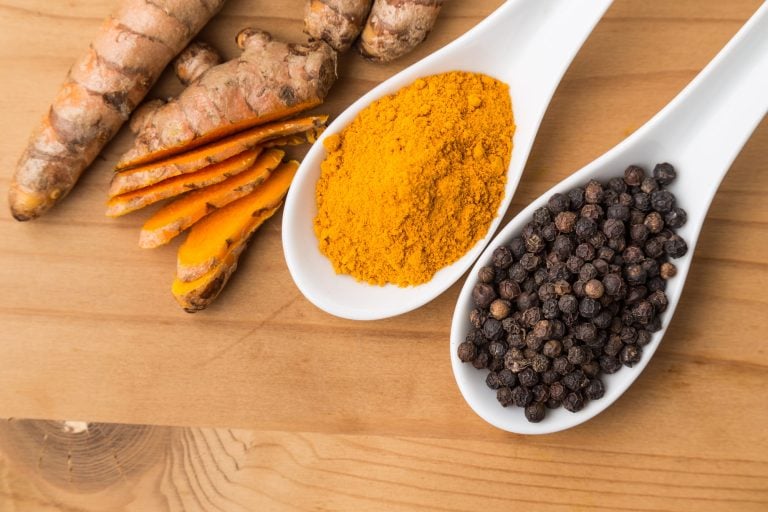

Have you wondered why traditional recipes call for using turmeric powder in milk (instead of water) or putting it in oil while making a curry? Curcumin’s poor absorption has been known for ages and various methods have been tried to enhance its bioavailability.
Traditional dietary practices involve taking curcumin with digestible lipids, such as milk, or heating curcumin in oil and then mixing it with food.
Innovative nutrient delivery techniques look beyond adjuvants and conventional dietary practices to enhance curcumin’s bioavailability. Some of the common techniques include liposomal encapsulations, powder nanoparticles, and phospholipid complexes.
Tetrahydrocurcumin, a primary metabolite of curcumin, displays pharmacological activities similar to curcumin, but it is more stable and bioavailable. As a result, tetrahydrocurcumin is easily absorbed into the gastrointestinal tract.
Research suggests that tetrahydrocurcumin is more bioactive than curcumin and appears to be a superior antioxidant because of its enhanced bioavailability11.
The poor natural bioavailability of curcumin is due to several factors, including —
Although adjuvants, such as piperine and turmeric oil, can inhibit or delay curcumin metabolism, innovative formulations offer longer circulation, enhanced permeability, and resistance to metabolic processes.
How do you identify an innovative curcumin supplement formulation? Read the product label, and if it says the formulation contains liposomes, micelles, nanoparticles, or phospholipid complexes, then it is an innovative supplement formulation.
TetraCumin,® developed by Tesseract Medical Research, is an innovative curcumin formulation. Why?
Tesseract’s nutrient delivery technology makes TetraCumin® an excellent curcumin nutritional supplement.
Tesseract’s CyLoc® technology encases each curcumin molecule in a dextrin fiber delivery cage to mask the unpalatable taste while maintaining its molecular integrity during transit through the stomach. Tesseract’s DexKey® technology releases the tetrahydrocurcumin molecules at the desired point in the intestinal tract, allowing for optimal absorption and bioavailability of each molecule.
As one of the best curcumin supplements, TetraCumin® makes curcumin a health-promoting reality, in lesser amounts than previously required, to better promote your health and wellness.*
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing add “solubility, “absorption and bioavailability, and micro-dosing multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support your musculoskeletal health.*
References:
1Unhapipatpong C, et al. Nutr Rev. 2025;83(8):1520-1536. doi:10.1093/nutrit/nuaf012
2Peng, Ying et al.Drug design, development and therapy vol. 15 4503-4525. 2 Nov. 2021, doi:10.2147/DDDT.S327378
3Gupta, Subash C et al.The AAPS journal vol. 15,1 (2013): 195-218. doi:10.1208/s12248-012-9432-8
4Dulbecco P, Savarino V. Therapeutic potential of curcumin . . . . World Journal of Gastroenterology vol. 19,48 (2013):9256-9270. doi:10.3748/wjg.v19.i48.9256
5,6Allegra A, et al. Int J Mol Sci. 2022;23(23):14710. Published 2022 Nov 25. doi:10.3390/ijms232314710
7Vera-Ramirez L, et al. Curcumin . . . . BioFactors (Oxford, England) vol. 39,1 (2013):88-100. doi:10.1002/biof.1057
8Xie YL, et al. Biomed Pharmacother. 2017;91:70-77. doi:10.1016/j.biopha.2017.04.070
9Akaberi M, et al. Adv Exp Med Biol. 2021;1291:15-39. doi:10.1007/978-3-030-56153-6_2
10Liu S, et al. Molecules. 2022;27(14):4400. Published 2022 Jul 8. doi:10.3390/molecules27144400
11Aggarwal BB, et al. Curcumin differs from tetrahydrocurcumin for molecular targets, signaling pathways and cellular responses. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 20,1 185-205. 24 Dec. 2014, doi:10.3390/molecules20010185
Article Summary:
Curcumin, the key metabolite derived from the underground stem of the turmeric plant, is well known for its health-promoting benefits. From mitigating oxidative stress to maintaining normal inflammatory responses in cells, curcumin promotes various health functions, including immune, gastrointestinal, and musculoskeletal health1,2. However, ingesting curcumin by itself does not lead to its associated health benefits because of its poor natural absorption, rapid metabolism, and rapid elimination from the body.
The unpleasant bitter taste of curcumin may be a barrier to achieving its use in supplement form. So, what are some of the most effective strategies to take curcumin as an oral supplement? This blog post answers several frequently asked questions about curcumin intake, how its bioavailability can be optimized, and why you should include an advanced curcumin supplement in your healthcare routine.
Although pure curcumin has immense health benefits, it is not chemically stable under physiological conditions. Before determining the effective ways to take curcumin, it is critical to understand the challenges to its absorption. The following are the causes of the poor absorption and bioavailability of curcumin:
To achieve curcumin’s health-promoting benefits, the best way to take curcumin is to overcome its palatability and solubility challenges. Bioavailability-enhancers, such as piperine, and lipid addition, such as turmeric oleoresin and turmeric oil, can enhance the bioavailability of curcumin to a certain extent.
The following table highlights several ways to take curcumin as an oral supplement:
| How Should You Take Curcumin as an Oral Supplement? | ||
|---|---|---|
| Consuming curcumin with a meal rich in healthy fats | It is a traditional dietary practice of taking turmeric, containing curcumin, with digestible lipids, such as milk, or heating curcumin in oil and then mixing it with food. Since curcumin is lipophilic, consuming it with a meal containing healthy fats enhances its absorption 5. | |
| Combining curcumin with enhancing agents | Piperine is a major active component of black pepper and can increase the bioavailability of curcumin by 2,000 percent. 6 | |
| Taking curcumin supplement formulations | Free curcumin molecules naturally cluster together, hindering cellular absorption. In contrast, curcumin formulations containing powder nanoparticles and loaded emulsions display higher cellular uptake and bioaccessability 7,8. | |
When considering taking a curcumin supplement, it is best to choose a formulation that enhances its absorption and bioavailability. Although curcumin is chemically unstable in the gastrointestinal environment, tetrahydrocurcumin, an active metabolite of curcumin, is both more stable and more water-soluble than curcumin. As a result, tetrahydrocurcumin displays enhanced absorption and bioavailability, making it more effective than curcumin9.
TetraCumin® is an innovative curcumin supplement developed by Tesseract Medical Research. It contains the bioactive tetrahydrocurcumin for helping to maintain a healthy inflammatory response and for promoting joint and muscle health.*
Tesseract’s proprietary CyLoc® – DexKey® nutrient delivery system further enhances tetrahydrocurcumin’s absorption, enveloping each tetrahydrocurcumin molecule in its smart delivery system to protect its integrity and to deliver each molecule at the desired point in the gastrointestinal tract.
The targeted delivery of nutrient molecules results in unprecedented absorption and enables micro-dosing, achieving faster physiological responses with lower amounts of the active ingredients. The targeted delivery, unprecedented absorption, and micro-dosing of the active ingredient make TetraCumin one of the best ways to achieve curcumin’s positive health outcomes.
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing add “solubility, “absorption and bioavailability, and micro-dosing multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective dose. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they can support your immune function and musculoskeletal health.*
References:
1Dehzad MJ, et al. Cytokine. 2023;164:156144. doi:10.1016/j.cyto.2023.156144
3Pan-On S, Dilokthornsakul P, Tiyaboonchai W. Trends in advanced oral drug delivery system for curcumin: A systematic review. J Control Release. 2022;348:335-345. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.048
4Pan-On S, Dilokthornsakul P, Tiyaboonchai W. Trends in advanced oral drug delivery system for curcumin: A systematic review. J Control Release. 2022;348:335-345. doi:10.1016/j.jconrel.2022.05.048
5Schönenberger KA, et al. The influence of food matrices on the bioavailability of curcuminoids from a dried colloidal turmeric suspension: a randomized, crossover, clinical trial. Food Funct. 2025;16(2):774-784. Published 2025 Jan 20. doi:10.1039/d4fo03414g
6Shoba G, et al. Planta Medica vol. 64,4 (1998):353-356. doi:10.1055/s-2006-957450
7Nelson KM, et al. Journal of Medicinal Chemistry vol. 60,5 (2017):1620-1637. doi:10.1021/acs.jmedchem.6b00975
8Luo H, Li Z, Yao M, McClements DJ, Xiao H. Impact of excipient emulsions made from different types of oils on the bioavailability and metabolism of curcumin in gastrointestinal tract. Food Chem. 2022;370:130980. doi:10.1016/j.foodchem.2021.130980
9Zhou M, Li R, Hua H, et al. The role of tetrahydrocurcumin in disease prevention and treatment. Food Funct. 2024;15(13):6798-6824. Published 2024 Jul 1. doi:10.1039/d3fo05739a
Article Summary:
When the body produces and accumulates an excess of free radicals, the balance between free radicals and antioxidants is disrupted. The resulting state of imbalance, known as oxidative stress, results in free radicals targeting cellular organelles, damaging lipids, nucleic acids, and proteins.
Antioxidants are compounds that inhibit oxidation and the production of free radicals, thereby protecting cells from damage caused by oxidative stress.* The body can generate its own antioxidants, such as glutathione, coenzyme Q10, uric acid, bilirubin, L-arginine, lipoic acid, melatonin, and transferrin. Some antioxidants, such as vitamins C and E, flavonoids, carotenoids, trace metals, and omega-3 and omega-6 fatty acids, can be consumed in the diet or taken as nutritional supplements.
Glutathione, a key antioxidant produced in the cells, consists of three amino acids — cysteine, glycine, and glutamic acid. Glutathione is present in almost every cell in the body at the same concentration as some other vital nutrients, such as potassium and glucose. Glutathione is the primary antioxidant, detoxifying agent, and critical redox regulator that helps maintain normal inflammatory responses,* making it the ‘master antioxidant.’
This blog post explains glutathione’s antioxidant properties, its bioavailability challenges, and why you should include an advanced glutathione supplement in your wellness plan or health routine.
A glutathione deficiency in the body is linked to cognitive decline, mitochondrial dysfunction, and other age-associated degeneration of health functions.* Recent research suggests that nutritional interventions, including amino acids, vitamins, minerals, and phytochemicals through diet and nutritional supplements, can help maintain an optimal circulating level of glutathione in the body.*1
Glutathione exerts its antioxidant effects primarily through reduction, conjugation, and interaction with other antioxidants.* The following table highlights glutathione’s antioxidant properties and how it eliminates toxins from the body and helps maintain the body’s antioxidant defense system.*2
| Glutathione’s Antioxidant Properties: An Overview | |
|---|---|
| Function | Description |
| Reduction |
|
| Conjugation |
|
| Interaction |
|
In addition, glutathione is involved in other beneficial cellular processes, such as protein folding, degradation of proteins with disulfide bonds, cell cycle regulation and proliferation, and beneficial cell death (apoptosis).*
Although glutathione is a critical antioxidant and is endogenously produced by the body, its absorption is generally poor when taken orally as a supplement. Intestinal enzymes break down glutathione during its transit through the gastrointestinal tract, leading to poor absorption and low bioavailability. Glutathione is conventionally known as a ‘difficult-to-absorb’ molecule. However, advanced nutrient delivery technologies have overcome glutathione’s solubility challenges.3
The efficacy of a glutathione nutritional supplement depends on its absorption and bioavailability.
Advanced supplement formulations utilize nanotechnology for the targeted delivery of glutathione molecules to achieve the desired health-promoting outcomes.
Tesseract Medical Research has developed SafeCell® — an innovative nutritional supplement formulation that contains an acetylated form of glutathione. SafeCell utilizes the proprietary CyLoc® – DexKey® nanomolecular nutrient delivery technology to enable unprecedented absorption of glutathione molecules.
The CyLoc® technology creates nano-sized particles of the active nutrient for better absorption. The accompanying DexKey® reactors release the CyLoc® molecules at the desired point in the intestinal tract. The resulting unprecedented absorption achieves glutathione’s potent antioxidant properties, making it a bioavailable reality.
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how SafeCell supports healthy liver function.*
Reference:
1Minich, Deanna M, and Benjamin I Brown. Nutrients vol. 11,9 2073. 3 Sep. 2019, doi:10.3390/nu11092073
2Averill-Bates DA. Vitamins and Hormones vol. 121(2023):109-141. doi:10.1016/bs.vh.2022.09.002
3Losada-Barreiro, Sonia et al. Pharmaceutics vol. 16,7 852. 25 Jun. 2024, doi:10.3390/pharmaceutics16070852
Article Summary:
Quercetin’s beneficial antioxidant and immunomodulatory properties make it a unique nutritional supplement.* The flavonoid, quercetin, found in various fruits and vegetables, is an antioxidant that helps maintain normal inflammatory responses in cells.* Quercetin promotes several health functions, including immune function, renal function, and cardiovascular function.
While quercetin is naturally available through dietary sources,, it is unfortunately also known for its poor absorption and limited bioavailability. This means that even if you are consuming a meal high in quercetin-containing foods ,, It is estimated that only 3-7 percent of quercetin glycoside (the most absorbable form of quercetin) is absorbed after ingesting at least 100 mg. Meaning, you are likely not absorbing enough quercetin to benefit from its healing properties from dietary sources alone.1
Various approaches have been explored to enhance quercetin’s absorption and bioavailability. For example, co-supplementation of quercetin with other nutrients can enhance quercetin’s solubility and thus benefit the body’s natural immune responses.* Advancements in nutrient delivery technologies, such as nanotechnology, have also enhanced quercetin’s bioavailability.
, When looking for the best quercetin supplement, what factors should you consider? This blog post explains key features of the best quercetin supplements and why you should include an advanced quercetin supplement formulation in your diet.
When considering including a supplement in your “wellness plan” or “health routine”, you want a formulation that helps you achieve quercetin’s many health-promoting benefits. The health-promoting benefits of the best quercetin supplements depends on the flavonoid’s solubility, absorption, and bioavailability.
The following table highlights the key features of the best quercetin supplement formulations for supporting optimal immune function:*
| Best quercetin supplement: What to Look for | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility | Quercetin’s solubility in aqueous solutions is low and pH-dependent. Supplement formulations that contain liposomes, nanoemulsions, and micelles can enhance quercetin’s water solubility. 2 | ||
| Absorption | Quercetin is absorbed in the upper segment of the small intestine. Its absorption varies based on the type of formulation. Formulations containing quercetin-loaded nanoparticles display better absorption than other delivery methods. | ||
| Bioavailability | Enhancing quercetin’s water solubility also increases its bioavailability. Phospholipid complexes of quercetin increase the compound’s water solubility approximately 13-fold, 3 thereby increasing bioavailability significantly compared to free quercetin. | ||
| Type of formulation | Oral, intravenous, intranasal, and topical administration of quercetin enhances its stability in the gastrointestinal environment and minimizes its intestinal degradation. In clinical studies, formulated quercetin displays a significant rise (more than 200%) in blood uptake compared to unformulated quercetin. 4 | ||
| Active nutrients | A quercetin supplement containing zinc and vitamins C and D3 exerts synergistic effects to better promote immune health.* Zinc enhances quercetin’s health-promoting benefits, whereas quercetin enhances zinc’s intracellular concentration. | ||
Looking at the product’s Supplement Facts label enables you to gather the required information about a quercetin supplement formulation, such as the active nutrients in the formulation, formulation type, delivery technology used, and recommended usage. You should also speak with a trusted healthcare provider to better understand the safety of a supplement formulation and the potential contraindications and interactions with any prescription medications or other supplements you are taking .
QuerciSorb® Immuphore SR, developed by Tesseract Medical Research, is a proprietary quercetin complex developed by Tesseract Medical Research. This advanced quercetin formulation contains other immuno-supportive compounds, such as zinc, vitamin C, and vitamin D3, to promote optimal immune function. Tesseract’s proprietary, groundbreaking CyLoc® – DexKey® nutrient delivery nanotechnology enables the optimal absorption of quercetin.
The CyLoc® technology encases individual quercetin molecules in its smart delivery system, and the accompanying DexKey® reactors release the molecules at the desired point in the intestinal tract to achieve maximum absorption. The unprecedented absorption of quercetin enables micro-dosing — using a lesser amount of quercetin than previously required to achieve a potent and immediate response.
The hypoallergenic, ionophore formula of QuerciSorb® Immuphore SR is one of the best quercetin supplements for promoting healthy immune function.* The formulation is manufactured following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMPs) and implements scientifically advanced analytical techniques and quality control systems to achieve the many health-promoting benefits of quercetin.*
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing a single or multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support optimal immune function.*
References:
1Li Y, et al. Nutrients vol. 8,3 167. 15 Mar 2016, doi:10.3390/nu8030167
2,3,4Solnier J, et al. Evidence-based Complementary and Alternative Medicine: eCAM vol. 2023 9727539. 10 Aug 2023, doi:10.1155/2023/9727539
Article Summary:
Quercetin is a type of flavonoid that provides a broad range of health benefits. It is well-known for its potent antioxidant activities and ability to help maintain the body’s natural inflammatory response.*
Flavonoids are a class of phytonutrients found naturally in various fruits and vegetables, such as berries, grapes, apples, cruciferous vegetables, onions, shallots, and tomatoes, as well as tea.
Due to the ability of flavonoids to neutralize free radicals, there is increasing scientific interest in understanding how flavonoids influence immune function in the body.
Below, we discuss quercetin’s immune-supporting properties and explore why you should consider including this antioxidant in your daily nutritional supplement regimen.
Quercetin naturally exists in various forms. For example, a form of quercetin that is particularly noted for its ability to enhance bioavailability through its increased water solubility, is querecetin glycoside.The glycoside form of quercetin, in particular, has enhanced water solubility, which makes it more easily absorbed in the body. This improved absorption enables quercetin to be more effective in reaching and positively influencing the body’s immune function.*
The following table highlights the specific ways quercetin’s immune system supportive properties work.
| Quercetin’s Immune-Support Properties | |
|---|---|
| Antioxidant Effects* | Immunomodulatory Effects* |
|
Free radical scavenger: Quercetin’s molecular structure is credited for its higher efficiency in scavenging free radicals. 1 |
Leukocyte up-regulator: Quercetin confers immune support by upregulating the activity of leukocytes 3.* Quercetin also exerts immuno-supportive activity by benefiting intracellular signaling pathways, enzymes, and membrane proteins.* |
|
Lipid oxidation inhibitor: As a potent lipid oxidation inhibitor, quercetin suppresses the start of chain oxidation and propagation of free radicals.* |
Mast cell stabilizer: A meta-analysis shows that quercetin’s role in stabilizing mast cells and gastrointestinal cytoprotective activities benefits immune function 4.* |
| Quercetin’s endogenous antioxidant properties mitigate 2 a range of cellular injury caused by free radicals.* | Studies find 5 that quercetin influences dendritic cell functions — the initiator and master regulator of antigen-specific immune responses.* |
.
Quercetin is primarily absorbed in the upper segment of the small intestine and subsequently metabolized in multiple organs, including the liver, small intestine, colon, and kidneys. However, quercetin is known for its naturally poor oral bioavailability:
| Although onions contain the highest natural source of quercetin, clinical trials show that after consuming an onion-rich meal, quercetin values peaked from baseline values after two hours and returned to baseline after 24 hours. This highlights how the body processes and eliminates quercetin relatively quickly. |
|---|
Quercetin absorption depends on its chemical structure — the presence of associated sugar or glycosyl group. The absence of glycosyl group lowers its water solubility and absorption.
| Only 3-17 percent of quercetin glycosides, the most absorbable form, is absorbed in healthy individuals who ingested at least 100 mg 8. |
|---|
How does quercetin support immune function? We have now discussed the antioxidant’s immune-supportive properties, but what is the best quercetin supplement to include in your diet?
QuerciSorb® Immuphore SR, developed by Tesseract Medical Research, is an innovative nutritional supplement formulated with a soluble form of quercetin that supports healthy immune function.* Zinc (as zinc picolinate), vitamin C (as ascorbic acid), and vitamin D (as cholecalciferol) are other bioactive and bioavailable ingredients in this hypoallergenic formulation that further support optimal immune function.*
Tesseract’s proprietary CyLoc – DexKey® nutrient delivery nanotechnology achieves quercetin’s benefits for promoting optimal immune function.*
The resulting optimal absorption of each QuerciSorb molecule makes it a bioavailable reality in achieving optimal immune function.*
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing a single or multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support immune health.*
References:
1Rice-Evans CA, et al. Free Radical Research vol. 22,4(1995):375-383. doi:10.3109/10715769509145649
2Mlcek J, et al. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 21,5 623. 12 May 2016, doi:10.3390/molecules21050623
3,4Chirumbolo S. Inflammation & Allergy Drug Targets vol. 9,4 (2010):263-285. doi:10.2174/187152810793358741
5Huang RY, et al. Journal of Immunology (Baltimore, Md.:1950) vol. 184,12(2010):6815-6821. doi:10.4049/jimmunol.0903991
6McAnlis GT, et al. European Journal of Clinical Nutrition vol. 53,2(1999):92-96. doi:10.1038/sj.ejcn.1600682
7Sahib HB, et al. Advances in Virology vol. 2022 1575605. 8 Jun 2022, doi:10.1155/2022/1575605
8Frenț, Olimpia-Daniela et al. International journal of molecular sciences vol. 25,22 12091. 11 Nov. 2024, doi:10.3390/ijms252212091
9Ramzan N, et al. Biometals. 2025 May 22. doi: 10.1007/s10534-025-00696-4. Epub ahead of print. PMID: 40402366.
Article Summary:
When it comes to the pillars of our wellness, a healthy gut is essential.. The intestinal tract is the largest immune-regulating organ in the body, and the stable and balanced state of microbes is a prerequisite to maintaining various physiological roles. The loss of gut microbiome/microbial diversity is linked to several adverse health conditions.
The impact of nutrition on the composition of gut microbiota is well-documented1. Diet is a driving factor in shaping human gut microbiota composition and function. There is growing interest in targeting the human gut microbiota through diet and nutritional approaches to promote overall gastrointestinal health.
This blog post explains quercetin’s gut health-supportive properties and why you should include an advanced quercetin supplement in your diet.
The intestine is perpetually exposed to both good and bad gut microbes and their metabolites, resulting in a close correlation between the intestine and human health. Oxidative stress and adverse inflammatory responses in the intestinal tract are linked to several adverse gastrointestinal conditions.
Typically, the cells of the gut wall are pressed tightly against each other, creating what are called tight junctions. These tight junctions prevent the gut’s contents from leaking into the bloodstream. However, when these tight junctions become disrupted (causing intestinal permeability), the immune system will upregulate an inflammatory response to counter the undigested food particles, bacteria, and toxins leaking into the bloodstream. Such unbalanced and adverse inflammatory responses negatively affect gut health.
Quercetin, a flavonoid naturally found in many fruits and vegetables in our diet, beneficially influences the gut environment and helps regulate the gut microbiota. Quercetin’s antioxidant properties and its ability to help maintain normal inflammatory responses in the gut hold immense positive potential to address gut health.
The following table highlights how quercetin’s gut health-supportive properties promote gastrointestinal health:
| System | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Quercetin’s Gut Health-Supportive Properties | |
| Limiting the production of pro-inflammatory cytokines* | Quercetin has been found to limit oxidative stress and help maintain normal inflammatory responses in lung epithelial cells.1 |
| Enhancing expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes* | As a flavonoid with antioxidant properties, quercetin scavenges free radicals and enhances the expression of endogenous antioxidant enzymes, such as glutathione peroxidase, catalase, and superoxide dismutase.2 |
| Modulating gut microbial diversity and richness* | Quercetin modulates gut microbial diversity and richness by promoting the proliferation of beneficial bacteria and suppressing harmful pathogens, maintaining healthy intestinal flora.3 |
Additionally, quercetin is considered a prebiotic— a class of nutrients that beneficial gut microbes feed on. Prebiotics pass through the digestive system, promoting the growth and activity of the beneficial microbes in the digestive tract4.
While quercetin is generally present in our daily diet, the quantity of quercetin contained in food products may not result in meaningful gastrointestinal benefits. In addition, quercetin’s naturally poor absorption and low bioavailability hinder its efficacy in promoting gut health.
QuerciSorb® Immuphore SR, developed by Tesseract Medical Research, is an innovative nutritional supplement formulated with an optimally soluble form of quercetin that supports healthy gastrointestinal function.* Zinc (as zinc picolinate), vitamin C (as ascorbic acid), and vitamin D (as cholecalciferol) are other bioactive and bioavailable ingredients in this hypoallergenic formulation that support the gut’s optimal functioning.*
Tesseract’s proprietary CyLoc – DexKey® nutrient delivery nanotechnology achieves quercetin’s gut health-supportive properties.* The CyLoc® technology surrounds each quercetin molecule in its own smart delivery system to protect the molecule from too rapid degradation during transit through the stomach. The accompanying DexKey® reactors release each molecule at the desired point in the intestinal tract for optimal absorption.
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing a single or multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support gastrointestinal health.*
References:
1Sul OJ, Ra SW. Molecules. 2021 Nov 17;26(22):6949. doi: 10.3390/molecules26226949. PMID: 34834040; PMCID: PMC8625571.
1Forney LA, et al. International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 19,3 895. 17 Mar 2018, doi:10.3390/ijms19030895
2Xu D, et al. Molecules (Basel, Switzerland) vol. 24,6 1123. 21 Mar 2019, doi:10.3390/molecules24061123
3Lin R, et al. Frontiers in Microbiology vol. 10 1092. 16 May 2019, doi:10.3389/fmicb.2019.01092
4Majid, Ishrat, et al. Food Chemistry Advances, vol. 4, 2024, p. 100725, https://doi.org/10.1016/j.focha.2024.100725. Accessed 4 Aug. 2025.
Are you wondering about how to select the right berberine supplement from a variety of commercially available products? Get the answers to common questions about the best berberine supplement based on the ingredient, delivery technology, bioavailability enhancement, and absorption. Use the links below to jump ahead to different topics on the page.

Although berberine is naturally found in the roots, rhizomes, and stem bark of plants like the barberry tree, it is not typically consumed in the average diet.. Given berberine’s broad range of health-supportive properties–including its role in metabolic, cardiovascular, and cellular health–regular supplementation can be a valuable way to ensure consistent intake.*
| Why Do You Need A Berberine Supplement? | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| For enhanced safety: | Raw berberine displays poor safety due to variable alkaloid content, whereas supplements can be formulated to enhance berberine’s safety profile by purified extraction. | ||
| For enhanced palatability: | Berberine has a distinctive bitter taste that can inhibit user compliance for some. Newer supplement formulations enhance the palatability of berberine for oral intake. | ||
| For better absorption: | Raw berberine displays poor membrane permeability. Berberine supplements address the shortcomings of unformulated berberine by optimizing solubility and absorption. | ||
The health-promoting benefits of berberine are attributable to the following factors:
Research studies have established the beneficial impact of berberine supplements on maintaining healthy blood glucose levels, lipid levels, and inflammatory markers.*
The following are some of the key uses of berberine supplements for supporting optimal health functions.
| System | Benefits |
|---|---|
| Endocrine Health* | Berberine supplements help address irregular periods and infertility arising from hormonal imbalance in women1. Berberine has been found to enhance insulin sensitivity and regulate lipid metabolism to promote healthy weight management in affected females2. |
| Cardiovascular Health* |
Various studies have established the
potential benefits of berberine for providing nutritional support in diabetes
.3 Berberine supplements support normal lipid metabolism, which can reduce low-density lipoprotein (LDL) levels and promote cardiovascular health. Normal glucose metabolism , including promoting insulin secretion and moderating intestinal absorption of glucose.* A meta-analysis overviewing the benefits of berberine found a positive relationship between berberine supplementation and positive healthcare outcomes in individuals with Type 2 Diabetes Mellitus4. |
| Immune Health* | Berberine supplements help maintain immune health by up-regulating beneficial cell-mediated immune responses.* |
| Hepatic Health* | Berberine supplements promote optimal liver detoxification — By decreasing glucose generation from non-carbohydrate precursors.* By enhancing ammonia detoxification in the liver.* |
| Neuro-Hormonal System* | Berberine supplements optimize the benefits of exercise and support healthy weight management by limiting exercise-induced exhaustion and muscle damage incurred during exercise .* |
| Gastrointestinal Health* | Berberine supplements promote a balanced and healthy gut microbiota, particularly by enhancing the growth of the bacteria that produce short-chain fatty acids. |
Berberine’s naturally low bioavailability has caused the research community to explore ways to increase its concentration in the blood.
Although injecting berberine offers a direct approach to enhancing its bioavailability by bypassing its breakdown in the gastrointestinal tract, injecting berberine can lead to adverse side effects. This makes oral intake of berberine a more popular and safer approach.
As commercially available nutritional supplements, berberine supplements are available in different forms, including —
When considering what are the best berberine supplements, you are looking for optimal absorption and bioavailability. So, which berberine ingredient makes the best berberine supplement?
Certain berberine supplement forms have an intensely bitter taste, which may impede user compliance. oor palatability of berberine supplements can be due to:
Berberine’s naturally bitter taste, combined with the activation of bitter taste receptors in the mouth, makes many berberine supplements unpalatable. A well-formulated berberine supplement can help overcome this issue by slowing the release rate of berberine molecules and reducing the concentration of free molecules in the saliva, thus masking berberine’s unpleasant taste.
Although berberine has immense health-promoting potential, developing a successful delivery system poses various challenges. Berberine’s naturally low bioavailability and poor absorption have led to the investigation of alternative modes and methods of nutrient delivery.
The following are some of the standard delivery technologies used in berberine supplements:
| Standard Delivery Technologies in Berberine Supplements | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Conventional Delivery |
Traditional delivery is targeted toward masking the bitterness of a relatively higher amount of berberine. Drawbacks: The berberine tablet coating process is not easy to control accurately. Coating thickness, uniformity, and tablet adhesion are major challenges. For sugar coating, the amount of coating materials is generally larger. |
||
| Polymer-Based Delivery |
Encapsulating berberine in polymers, such as sodium alginate and calcium alginate, is a popular approach to enhance absorption. Drawbacks: Polymer-based drug delivery has certain limitations, including low drug loading capacity and cellular toxicity. |
||
| Lipid-Based Delivery |
This involves encapsulating berberine in a lipid-based microscopic bubble to prevent its degradation in the gastrointestinal tract. Drawbacks: Lipid-based delivery is susceptible to enzymatic degradation of active nutrients, displays physical and chemical instability, and has poor oral bioavailability. |
||
| Nano-Based Delivery |
These formulations use nanotechnology, including cyclodextrins, nanogel, nanoparticles, and nano-suspension, for targeted delivery of berberine at the desired point in the intestinal tract. Advantages: A nano-formulated berberine supplement is better absorbed in lesser amounts than required with other delivery methods, while masking the unpalatability of berberine to better achieve user compliance. |
||
| The absolute bioavailability of raw berberine is as low as 0.68 percent. |
|---|
Studies2 reveal that less than five percent of oral intake of berberine is absorbed in the intestine in 2.5 hours of its ingestion. It is berberine’s poor natural bioavailability that hinders its efficacy in supplemental form.
The following are key factors that affect the absorption of berberine:
| Factors Affecting Berberine Absorption | |||
|---|---|---|---|
| Solubility and permeability | Berberine’s low water solubility hinders berberine molecules from moving across the plasma membrane of intestinal cells. | ||
| Stability in the GI tract environment | The tendency of berberine molecules to self-aggregate in a low pH environment leads to poor absorption in the stomach and small intestine. | ||
| Extensive Metabolism | Berberine undergoes extensive intestinal first-pass elimination, with a majority of berberine being metabolized in the liver. | ||
The short-term safety profile of berberine is well-established, although there is limited data on its effects on pregnant and breastfeeding women. Furthermore, berberine can cause mild or infrequent side effects or have potential contraindications when taken with certain prescription medications.
The following table highlights some of the common side effects of berberine supplements:
| Berberine Supplement Side Effects | ||
|---|---|---|
| Gastrointestinal side effects | Constipation, diarrhea, flatulence, and stomach pain. | |
| Low glucose level | Prolonged intake of a berberine supplement in high amounts might cause a low glucose level. | |
| Potential contraindications | Berberine supplements might cause adverse effects when taken with a medication that is metabolized via the CYP enzymes. | |
The possible side effects of a berberine supplement depend on the delivery route (type of formulation) and the duration of intake. Hence, it is recommended to consult your healthcare provider before including a berberine supplement in your diet or taking one with a prescription medication.
When looking for the best berberine supplement, you should consider:
Tesseract Medical Research’s BerberActiv® is an innovative, palatable, and hypoallergenic berberine supplement containing a berberine extract derived from the root of the Berberis aristata plant. The following factors make BerberActiv an excellent choice as a berberine supplement.
BerberActiv® is manufactured following Good Manufacturing Practices (GMP) that implement scientifically advanced analytical techniques and quality control systems. This ensures the supplement formulation’s unparalleled efficacy in supporting overall health and wellness.
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing a single or multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support immune health.
Citations:
1Di Pierro F, Sultana R, Eusaph AZ, et al. Front Pharmacol. 2023;14:1269605. Published 2023 Nov 21. doi:10.3389/fphar.2023.1269605
2Rondanelli M, Infantino V, Riva A, et al. Arch Gynecol Obstet. 2020;301(1):53-60. doi:10.1007/s00404-020-05450-4
3Guo J, et al. Oxidative medicine and cellular longevity vol. 2021 2074610. 15 Dec. 2021, doi:10.1155/2021/2074610
4Moon JM, et al. Nutrients vol. 14,1 124. 28 Dec. 2021, doi:10.3390/nu14010124
Get the answers to common questions about how to choose the best CoQ10 supplement, including the different forms of CoQ10 and factors you should consider when determining the right CoQ10 supplement formulation for your health. Use the links below to jump ahead to different topics on the page.
Coenzyme Q10 – or CoQ10 – a lipid-soluble antioxidant your body makes, plays a critical role in cellular energy production.* Its concentration is particularly high in organs that have high metabolism rates, such as the heart, kidneys, and liver.
The CoQ10 level in your body depletes as you age, from the influence of certain medications, such as statins, or due to different pathological conditions a person might have. Although a CoQ10 deficiency can be partially addressed through a balanced diet of CoQ10-rich foods like oily fish, organ meats, and whole grains, they may not be sufficient to maintain an optimal level of CoQ10 in the body. In such cases, a CoQ10 supplement can help support cellular energy production and overall health.*
CoQ10 plays a fundamental role in cellular bioenergetics, which enables CoQ10 to address pathologies in tissues with high metabolic requirements, such as the heart muscle.* In addition to energy production, CoQ10 is an antioxidant (a free radical scavenger) that protects cellular components from the adverse effects of oxidative stress.*
The following table summarizes how including a CoQ10 nutritional supplement in your diet will support various health functions:
| Health Function | CoQ10 Supplement Benefits |
| Heart | Helps maintain optimal cholesterol levels and normal blood pressure.*Helps limit oxidative stress to protect heart muscle tissues.*Helps address the side effects of statin medications, such as muscle aches and weakness.* Learn more about choosing between CoQ10 and fish oil for supporting heart health. |
| Skin | Promotes healthy skin by enhancing the cellular metabolism of aging skin cells.* Stimulates collagen synthesis.* Helps maintain the stability and flexibility of the skin.*Learn more about coenzyme Q10’s skin benefits.* |
| Reproductive Health | Enhances the quality of the oocyte — the immature egg cell.*Supports a favorable environment for the development of ovarian follicles.*Learn more about CoQ10’s benefits for women and CoQ10’s beneficial effects on the menstrual cycle.* |
| Immune System | Helps maintain the body’s natural inflammatory response.*Plays a critical function within the lysosome, the organelle central to immune function.*Supports optimal functioning of immune cells with adequate cellular energy production.* Learn more about selecting between quercetin and CoQ10 for supporting immune health.* |
| The whole body content of CoQ10 is only about 500 – 1,500 milligrams. |
Based on no-observed-adverse-effect-level (NOAEL) studies1 on CoQ10, the acceptable daily intake of CoQ10 is 12 mg/kg/day, which translates to 720 mg/day for a person weighing 132 pounds.
However, it is worth noting there is no established minimum or maximum effective daily intake. In clinical trials exploring the beneficial effects of CoQ10 on the heart, 100 – 400 mg of CoQ10 was given to the trial participants.
| The average CoQ10 amount necessary to attain an optimal blood level of > 2.5 mcg/mL is 200 mg taken twice daily with a meal.2 |
Commercially available single CoQ10 capsules contain between 30-600 mg of CoQ10.
Because CoQ10 is produced naturally in the body, additional oral supplementation is usually well-tolerated. However, infrequent and generally mild side effects have been reported.
The following table highlights some of the potential side effects of CoQ10 supplementation:
| Potential Side Effects of CoQ10 Supplementation | ||
| Infrequent effects | Gastrointestinal side effects, including nausea, stomach upset, vomiting, or diarrhea. | |
| Rare effects | Headache, fatigue, heartburn, irritability, dizziness | |
| Potential contraindications | CoQ10 supplements might interact with prescription medicines for blood thinning, kidney disorders, liver disorders, and glucose metabolism. | |
Commercially available CoQ10 supplements are generally available in the form of ubiquinone or ubiquinol. There is ongoing debate about the most effective form of CoQ10 supplementation. CoQ10 exists in three oxidation states:
The ubiquinone and ubiquinol forms coexist in the body and regenerate each other through sequential redox reactions. Ubisemiquinone is a highly unstable, intermediate form of CoQ10. Ubiquinone and ubiquinol are interconverted based on the body’s need for the optimal functioning of its cells. Under the action of gastric acid, ubiquinol is oxidized to ubiquinone before it is absorbed into the body.
Regardless of the initial dietary intake form of CoQ10 (either ubiquinone or ubiquinol), it remains in the blood and in the lymph in the ubiquinol form. The following table highlights some of the key differences between the ubiquinone and ubiquinol forms of CoQ10:
| Ubiquinone or Ubiquinol—Which One Works Better? | ||
| Ubiquinone | Ubiquinol | |
| Chemical form | The oxidized form of CoQ10 (CoQ10) | The reduced form of CoQ10 (CoQ10H2) |
| Function | Involved in the electron transport chain in mitochondrial inner membranes for energy production. | Antioxidant protection to cellular membrane lipids and lipoprotein lipids present in circulation. |
Several clinical studies establish there is no significant difference in the bioavailability of ubiquinone and ubiquinol.
CoQ10 supplements are mostly available for oral intake in the form of chewable tablets, capsules, liquid syrups, and oral sprays. However, CoQ10’s poor natural absorption in the intestine adversely affects its efficacy through the oral route.
| Only approximately 3-6% of orally administered CoQ10 is absorbed in humans.3-5 |
The poor oral bioavailability and absorption of CoQ10 in supplements are due to:
CoQ10 nutritional supplements are generally produced through the yeast fermentation process. However, not all CoQ10 supplements are developed equally for optimal efficacy. When it comes to determining the best CoQ10 supplement to include in your diet, the following factors should be considered:
| The bioavailability and absorption of CoQ10 depend on the type of supplement formulation. |
Conventional CoQ10 formulations have failed to enhance CoQ10’s bioavailability. Various novel approaches6 as an alternative to traditional delivery methods have been implemented to enhance CoQ10’s solubility, including:
Among these novel approaches, encasing CoQ10 with cyclodextrins can significantly enhance CoQ10’s absorption and bioavailability, suggesting that this delivery process is superior to formulations that feature only uncomplexed CoQ10.
The following are frequently asked questions about how to choose the best CoQ10 supplement:
Although the safety profile of CoQ10 is well-established, it can interact with prescription medicines. Consult your healthcare provider before including a CoQ10 supplement in your diet.
Because there is limited safety data on the use of CoQ10 during pregnancy and breastfeeding, it is recommended to consult your healthcare provider before taking a CoQ10 supplement during pregnancy or when breastfeeding.
When considering the best CoQ10 supplement to choose, keep in mind that the supplement’s efficacy will be determined by the delivery technology used in the formulation.
Tesseract Medical Research’s CoQ10 Pro® is an innovative CoQ10 nutritional supplement that uses the proprietary CyLoc® – DexKey® nanotechnology nutrient delivery for the unparalleled absorption of billions of CoQ10 molecules in the intestinal tract. This unprecedented absorption of CoQ10 enables micro-dosing—taking CoQ10 in an amount much smaller than previously required to accomplish the desired health-promoting benefits.
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing bioavailability and absorption, and micro-dosing of multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Visit our website for more information about how Tesseract’s products can support your cardiovascular health.*
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing bioavailability and absorption, and micro-dosing of multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Visit our website for more information about how Tesseract’s products can help support your cardiovascular health
References:
1Hidaka T, et al. Safety assessment of coenzyme Q10 (CoQ10). BioFactors (Oxford, England) vol. 32,1-4 (2008):199-208. doi:10.1002/biof.5520320124
2Raizner AE. Coenzyme Q10. Methodist DeBakey Cardiovascular Journal vol. 15,3(2019):185-191. doi:10.14797/mdcj-15-3-185
3Bhagavan HN, Chopra RK. Coenzyme Q10: absorption, tissue uptake, metabolism and pharmacokinetics. Free Radic Res. 2006;40(5):445-453. doi:10.1080/10715760600617843
4López-Lluch G, Del Pozo-Cruz J, Sánchez-Cuesta A, Cortés-Rodríguez AB, Navas P. Bioavailability of coenzyme Q10 supplements depends on carrier lipids and solubilization. Nutrition. 2019;57:133-140. doi:10.1016/j.nut.2018.05.020
5Mantle D, Dybring A. Bioavailability of Coenzyme Q10: An Overview of the Absorption Process and Subsequent Metabolism. Antioxidants (Basel). 2020;9(5):386. Published 2020 May 5. doi:10.3390/antiox9050386
6Pastor-Maldonado CJ, et al. Coenzyme Q10: Novel formulations and medical trends. International Journal of Molecular Sciences vol. 21,22 8432. 10 Nov. 2020, doi:10.3390/ijms21228432
Article Summary:
Berberine, found in the roots, rhizomes, and stem bark of plants such as Berberis aristata (tree turmeric), Berberis aquifolium (Oregon grape), and Berberis vulgaris (barberry), is known for having multiple health-promoting benefits.*
Berberine’s antioxidant properties and its role in helping maintain the body’s natural inflammatory response have long been associated with supporting good endocrine health, with particular benefits related to glucose metabolism.*
Below, we discuss berberine’s glucose support properties and how including a berberine supplement in your diet can help maintain optimal glucose metabolism in your body.
Glucose is integral to energy production in the body. Once in circulation, glucose is transported into cells and metabolized to eventually produce adenosine triphosphate (ATP) — the primary energy currency of the cell.
Glucose metabolism refers to the various biochemical processes by which the body utilizes glucose to produce energy. Several different organs participate in glucose metabolism, including the nervous system, pancreas, liver, gut, and adipose cells.
Let’s look at how glucose metabolism works.
Let’s look at how berberine’s glucose support properties benefit glucose metabolism.
Berberine’s Glucose Support Properties | ||
| Addressing Insulin Resistance* | Berberine enhances1 the physiological stimulation of glucose through a cascade reaction of insulin-like growth factor-1 (IGF-1), a critical stimulant that induces insulin secretion and reduces insulin resistance.* Berberine also enhances the sensitivity of the liver, muscle tissues, and fat to insulin.* | |
| Promoting Insulin Secretion* | Berberine’s antioxidant properties protect pancreatic islet cells and promote insulin secretion by enhancing the activation of the cyclic adenosine monophosphate (cAMP) signal pathway.* | |
| Inhibiting Gluconeogenesis* | Berberine promotes2 glucose uptake and inhibits gluconeogenesis by inhibiting the SIRT3 protein and regulating mitochondria-related pathways.* | |
| Stimulating Glycolysis* | Berberine-induced activation of the AMP-activated protein kinase (AMPK) signaling pathway is likely3 a consequence of mitochondrial inhibition of glucose oxidation, which stimulates glycolysis.* | |
| Limiting Intestinal Absorption of Glucose* | Berberine reduces4 the activity of the enzyme disaccharidase and inhibits the digestion of carbohydrates in the intestine.* | |
| Modulating Gut Microbiota* | Berberine positively influences5 the gut microbiota, enriching the population of butyrate-producing bacteria.* | |
Several clinical studies suggest berberine’s beneficial effects on glucose metabolism.* However, berberine’s naturally poor bioavailability and bitter taste hinder its efficacy and pose challenges to user compliance. A supplement containing nano-formulated berberine shows more promising results than unformulated berberine.
BerberActiv® is a unique hypoallergenic berberine nutritional supplement developed by Tesseract Medical Research for quick and sustained release, as well as enhanced bioavailability. Tesseract’s proprietary CyLoc® – DexKey® nutrient delivery technology ensures targeted delivery of the berberine molecules in the intestinal tract for optimal absorption.
Tesseract’s CyLoc® technology isolates and encases each berberine molecule individually in a dextrin fiber matrix, creating nanosized particles. Tesseract’s DexKey® technology accompanies the CyLoc® molecules and breaks the dextrin fiber cage at the desired point in the intestinal tract to release one berberine molecule at a time for maximum absorption and efficacy.
This unprecedented absorption of berberine in your body translates to promoting optimal glucose metabolism, lipid metabolism, gastrointestinal health, and liver function.*
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing a single or multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support endocrine health.*
References:
1Li M, et al. Integrative analysis of metabolome and gut microbiota in diet-induced hyperlipidemic rats treated with berberine compounds. Journal of Translational Medicine vol. 14,1 237. 5 Aug. 2016, doi:10.1186/s12967-016-0987-5
2Zhang B, et al. Berberine promotes glucose uptake and inhibits gluconeogenesis by inhibiting deacetylase SIRT3. Endocrine vol. 62,3(2018):576-587. doi:10.1007/s12020-018-1689-y
3Yin J, et al. Berberine improves glucose metabolism through induction of glycolysis. American Journal of Physiology. Endocrinology and Metabolism vol. 294,1(2008):E148-156. doi:10.1152/ajpendo.00211.2007
4Liu L, et al. Berberine suppresses intestinal disaccharidases with beneficial metabolic effects in diabetic states, evidences from in vivo and in vitro study. Naunyn-Schmiedeberg’s Archives of Pharmacology vol. 381,4(2010):371-381. doi:10.1007/s00210-010-0502-0
5Zhang L, et al. Effects of berberine on the gastrointestinal microbiota. Frontiers in Cellular and Infection Microbiology vol. 10 588517. 19 Feb. 2021, doi:10.3389/fcimb.2020.588517
Article Summary
Short-chain fatty acids (SCFAs)—including butyrate, propionate, and acetate—are important metabolites produced in the lower intestinal tract through bacterial fermentation of undigested dietary fibers and resistant starch. Smaller amounts may also be derived from dietary proteins and the body’s own endogenous proteins.
Among the SCFAs, butyrate has gained significant scientific interest because of its essential role in supporting gastrointestinal health.* Several studies highlight the role of butyrate in upregulating immune function, as well as supporting a healthy inflammatory response in the gastrointestinal tract.* Furthermore, there is growing evidence of butyrate’s beneficial effect on brain function via the gut-brain axis.*
However, low dietary fiber intake can limit the gut’s production of SCFAs like butyrate, which can adversely affect both local and systemic GI inflammatory responses. For this reason, consuming a fiber-rich diet that promotes butyrate production–along with targeted butyrate supplementation–can be a valuable strategy for supporting a healthy gut microbiome and overall digestive health.*
The USDA recommends a daily dietary fiber intake of 25 grams for women and 38 grams for men. This recommended intake includes non-starch polysaccharides, non-digestible oligosaccharides, and resistant starch.
Fiber is a complex mixture of dietary residues, primarily carbohydrates, that are not digested or absorbed by the small intestine but are used instead as a food source by the colon microbiota.
The colonic microbiota is one of the body’s most metabolically active areas. SCFAs contribute up to 60-70 percent of the energy required by colonic epithelial cells and 5-15 percent of the human body’s total caloric requirements.
Although butyrate is the least abundant SCFA produced in the body, it is a major energy source for the colonocytes – the cells that line the colon.* Because the presence of undigested dietary fiber in the intestine and the production of butyrate are closely associated, it’s important to include high-fiber foods and butyrate-rich foods in your diet.
| Butyrate-Rich Foods To Add to Your Diet | ||
|
1
|
Legumes |
Cooked legumes are a great source of resistant starch. Letting legumes cool after cooking them can increase their resistant starch content due to retrogradation of starch molecules. Beans, peas, and lentils are also good sources of galactooligosaccharides. |
|
2
|
Whole Grains |
Oats, cooked and cooled rice, quinoa, wheat, rye, and other whole grains are good sources of resistant starch. |
|
3
|
Fruits & Vegetables |
Fruits like watermelon, pear, blueberries, mulberries, red currants, raspberries, and figs are rich in oligosaccharides. Plantains, green bananas, and cooked, cooled potatoes are good sources of resistant starch. White onions, green cabbage, red cabbage, scallions, leeks, garlic, broccoli, and kale are also high in oligosaccharides. |
|
4
|
Nuts & Seeds |
Chia seeds, almonds, pistachios, and sunflower kernels are rich in dietary fiber. |
|
5
|
Dairy Products |
Moderate dairy intake: The lactic acid bacteria in dairy foods like butter and parmesan cheese help break down milk fats and produce SCFAs, including butyrate. |
A well-balanced diet comprising the fiber-rich components above promotes a healthy gastrointestinal environment. However, not everyone can obtain or tolerate the amount of fiber needed to produce the required quantity of butyrate for optimal gut function.
Therefore, a butyrate supplement can easily and effectively fill any nutritional gaps and increase the level of butyric acid.*
When considering butyrate supplementation, it should be noted that not all nutritional supplements are alike. The efficacy of a butyrate supplement depends on whether it is formulated to optimize butyrate’s bioavailability, thus leading to enhanced absorption and augmenting the gut’s butyric acid level.*
ProButyrate®, a Tesseract supplement, is specifically designed to restore balance and stabilize the gut microbiome.* Tesseract’s revolutionary CyLoc® – DexKey® nutrient delivery technology envelops individual butyric acid molecules to ensure both their palatability and their optimal absorption throughout the GI tract, one molecule at a time. ProButyrate’s hypoallergenic formula yields overall positive health benefits and helps you take control of your gut health every day.*
The power of Tesseract supplements lies in enhancing palatability, maximizing solubility, absorption, and bioavailability, and micro-dosing a single or multiple nutrients in a single, highly effective capsule. Shop products on our website and learn more about how they support gastrointestinal health.*
Reference
1 Tan J, McKenzie C, Potamitis M, et al. Adv Immunol 2014;121:91-119. doi: 10.1016/B978-0-12-800100-4.00003-9. PMID: 24388214.